Maillard reaction was named after the French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard, who originally described the reaction between amino acids and sugars in 1912.
The chemical reaction which occurs between reducing sugars and principally free amino acids and peptides (usually from proteins) in the presence of heat that results in the browning of food while forming its distinctive flavor and aromas.
Why does it make everything taste delicious?
A guide to the Maillard Reaction
Further Reading on Maillard Reaction
Articles:
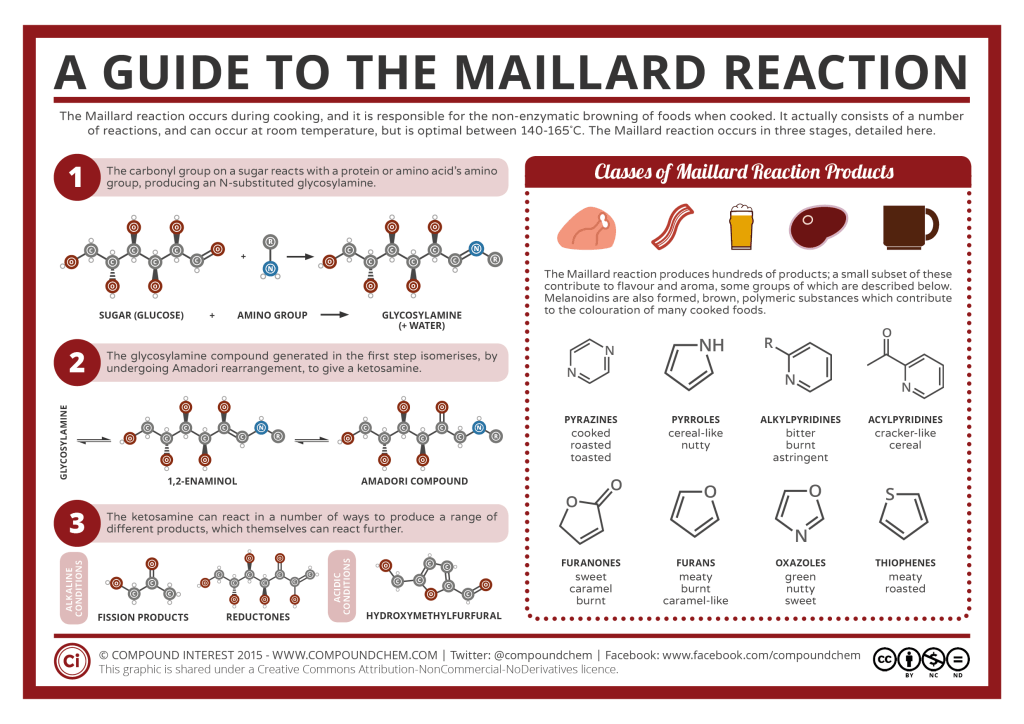
Compound Interest – Food Chemistry – The Maillard Reaction
Warwick University: Chemistry of Maillard Reaction
University of Bristol – School of Chemistry – The Maillard Reaction
Research:
Formation of flavour compounds in the Maillard reaction
Food chemistry: Acrylamide from Maillard reaction products
Analysis of Acrylamide, a Carcinogen Formed in Heated Foodstuffs
Food Processing and Maillard Reaction Products: Effect on Human Health and Nutrition
Effect of Emerging Processing Technologies on Maillard Reactions
Milk Production and Processing – Improving UHT processing and UHT milk products
Numerous research papers on Maillard reaction – The Maillard reaction is defined as “an array of non-enzymatic chemical reactions between carbonyl (primarily carbohydrates) and amino compounds of biological origin”.